- TSRL, Inc. | Prodrug & Infectious Disease | Preclinical ...
- Bcs Classification Database Query
- Biopharmaceutics Classification System - Wikipedia
BCS Class 2a drugs, weak acids that exhibit low solu-bilityonlyatlowpH.TheWHOrecommendedcriteria for such drug products would be rapid dissolution at pH 6.8 and a similar dissolution profile to the innova-tor product at pH 1.2, 4.5, and 6.8. Like the EMA, the. The BCS classification system is used to categorize drugs and serves to help anticipate whether drugs will have bioavailability/ bioequivalence problems. BCS classifies drugs according to their solubility and permeability. A drug is considered to have high solubility if drug substance at the highest dose strength for an immediate release formulation can be dissolved in. BCS archive database 1) The former NACE rev.1.1 business survey series (up to April 2010) continue to be available here-after ('total sector' and NACE rev.1.1 subsectors). All files are in WinZip format (size ranges from 100kb to 10Mb).

The “Waiver of In-vivoBioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System” is an FDA guidance document, which allows pharmaceutical companies to forego clinical bioequivalence studies, if their drug product meets the specification detailed in the guidance.
The principles of the BCS classification system can be applied to NDA and ANDA approvals as well as to scale-up and post approval changes in drug manufacturing. A waiver of In-vivo Bioavailability and Biioequivalence studies based on the BCS classification can therefore save pharmaceutical companies a significant amount of development time and reduce development costs.
TSRL, Inc. | Prodrug & Infectious Disease | Preclinical ...
The BCS classification system is based on the scientific rationale that, if the highest dose of a drug candidate is readily soluble in the average fluid volume present in the stomach (250 ml) and the drug is more than >85% absorbed, then the in vitro drug product dissolution profiles should allow assessment of the equivalence of different drug formulations. Solubility and dissolution can be easily measured in vitro. Extent of absorption has historically been determined by conducting mass balance studies both preclinically and clinically.
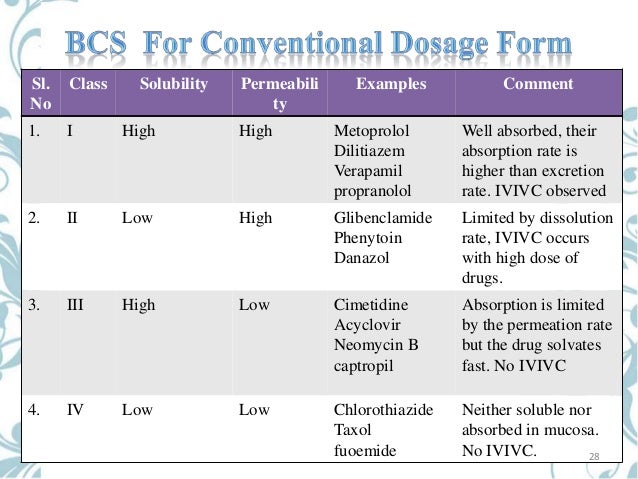
However, our work and that of our collaborators has demonstrated that the effective intestinal permeability (Peff) of therapeutic agents correlates well with total fraction absorbed in both humans, rats, and to a lesser extent in vitro tissue culture systems (1-5). Based on these studies a drug candidate can fall into one of four BCS categories, with category I, High Permeability and High Solubility, being the subject of the BCS guidance. The WHO has recently recommended biowaivers for Class III and some Class II drugs and AAPS-FDA scientific conferences have recommended biowaivers for Class III compounds as well.
References:
GL Amidon et al., Pharm Res Vol 12(3): 413-420, 1995
A Dahan et al., Molecular Pharmaceutics, Vol 10(11): 4378-4390, 2013 (http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/mp400485k)
X Cao et al, Pharm Res Vol 23(8):1675-1686, 2006
H Lennernas at al., Pharm Res Vol 14(5): 667-671, 1997
P Artursson and J Karlson, Biochem Biophys Res Comm. Vol175(3): 880-885, 1991

Bcs Classification Database Query

Biopharmaceutics Classification System - Wikipedia
For more information, please contact:
Gordon Amidon, PhD
TSRL, Inc.
540 Avis Drive, Suite A
Ann Arbor, MI 48108
Phone: (734) 663-4233 x222
E-mail: glamidon@umich.edu
